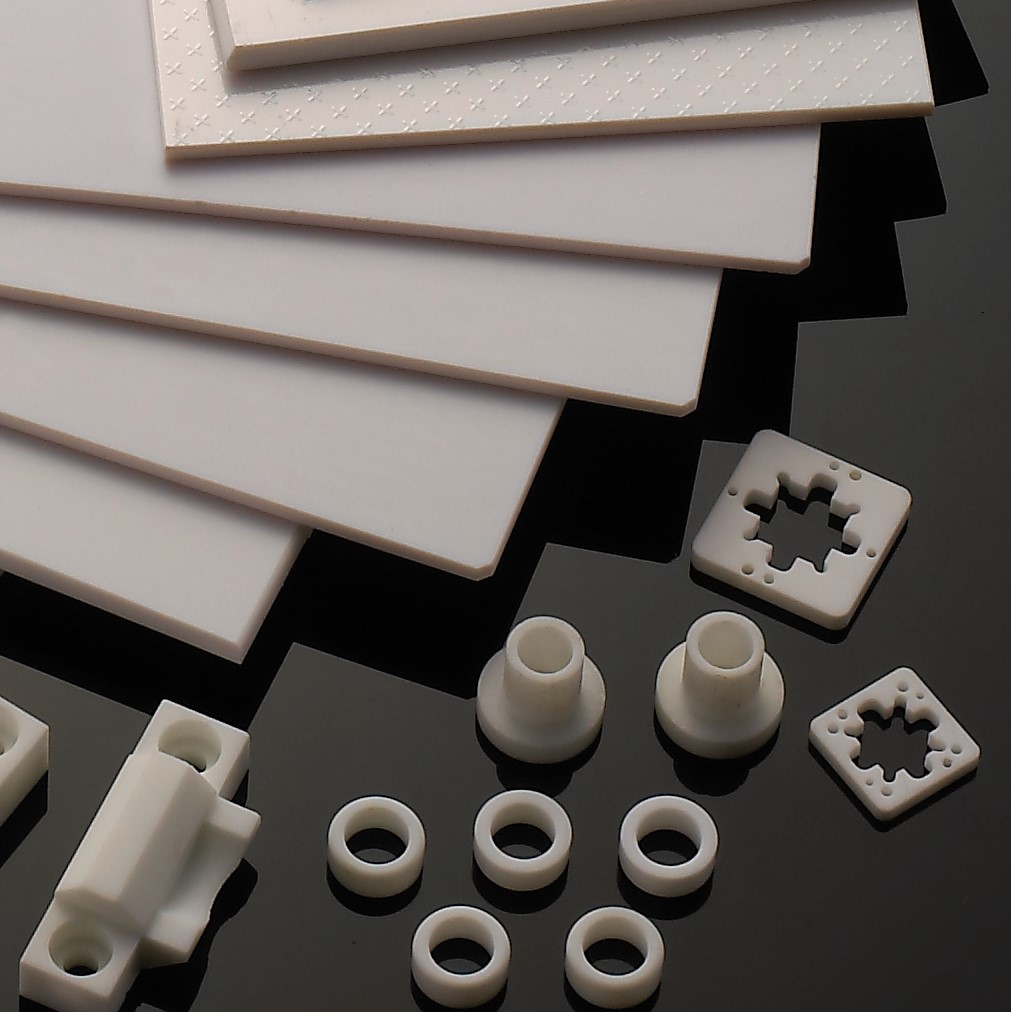
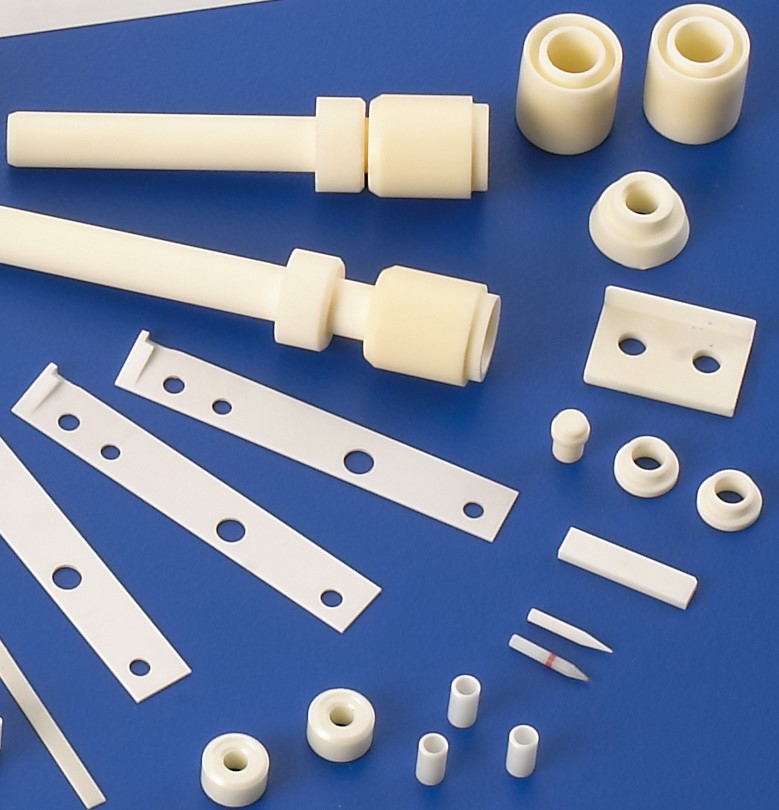
ZrO2
Material Characteristics
Under normal pressure, pure ZrO2 exists in three crystalline forms: monoclinic zirconia (m-ZrO2), tetragonal zirconia (t-ZrO2), and cubic zirconia (c-ZrO2). Typically, different types of stabilizers are added to produce various types of zirconia ceramics, such as partially stabilized zirconia (PSZ). When the stabilizers are CaO, MgO, or Y2O3, they are denoted as Ca-PSZ, Mg-PSZ, and Y-PSZ, respectively. Zirconia ceramics composed of metastable t-ZrO2 are called tetragonal zirconia polycrystal ceramics (TZP). If the stabilizers added are Y2O3 or CeO2, they are referred to as Y-TZP and Ce-TZP, respectively.
Material Applications
Structural Ceramics
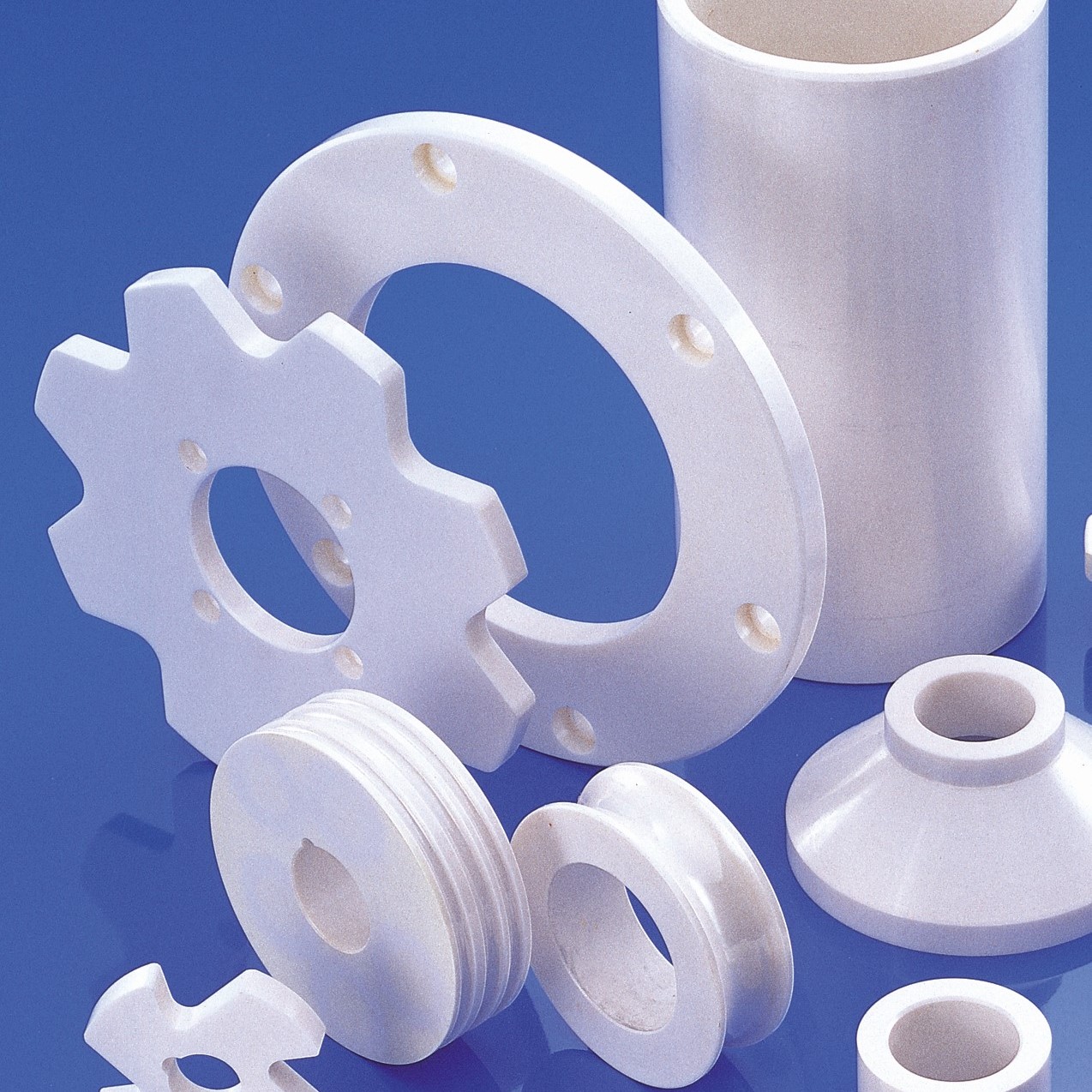
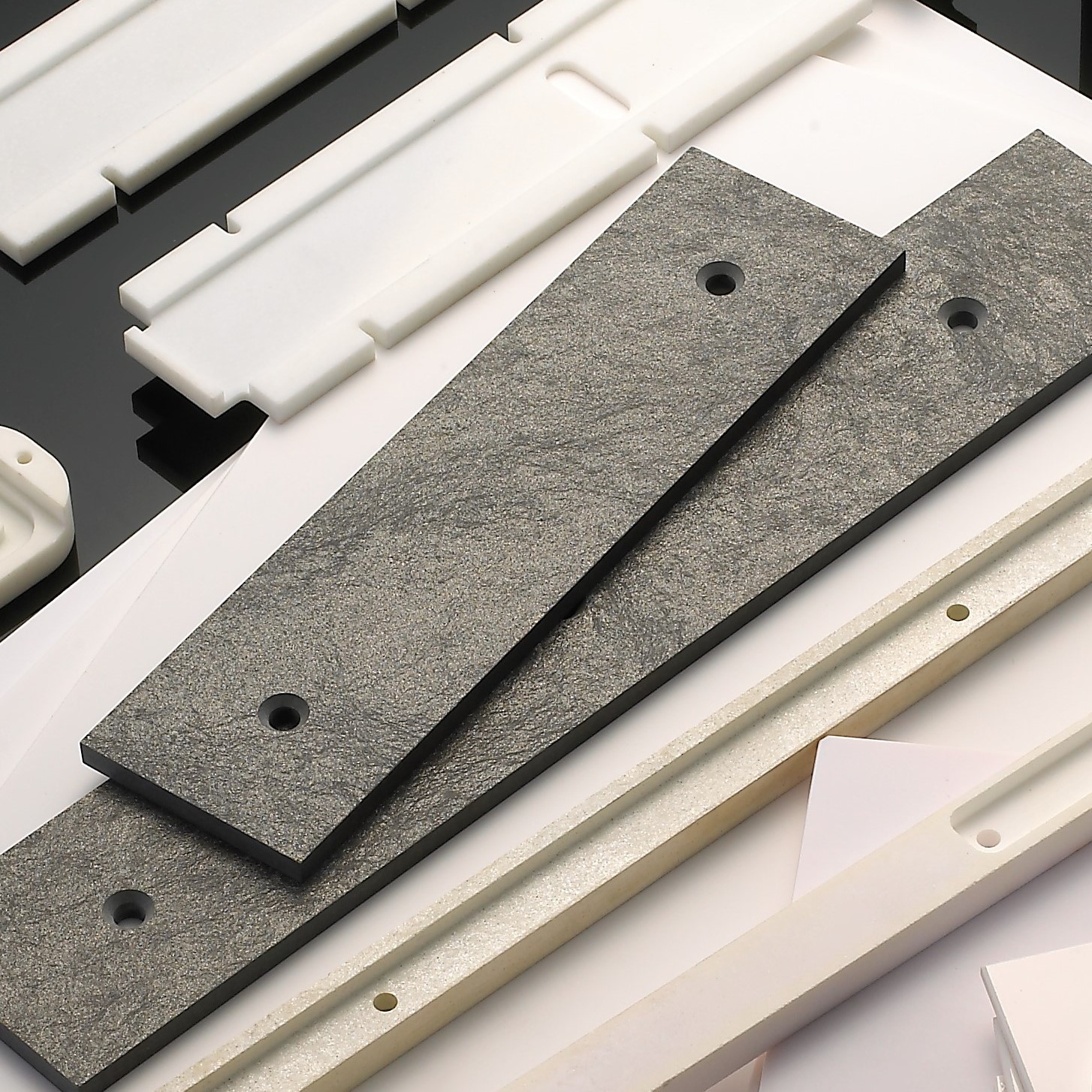
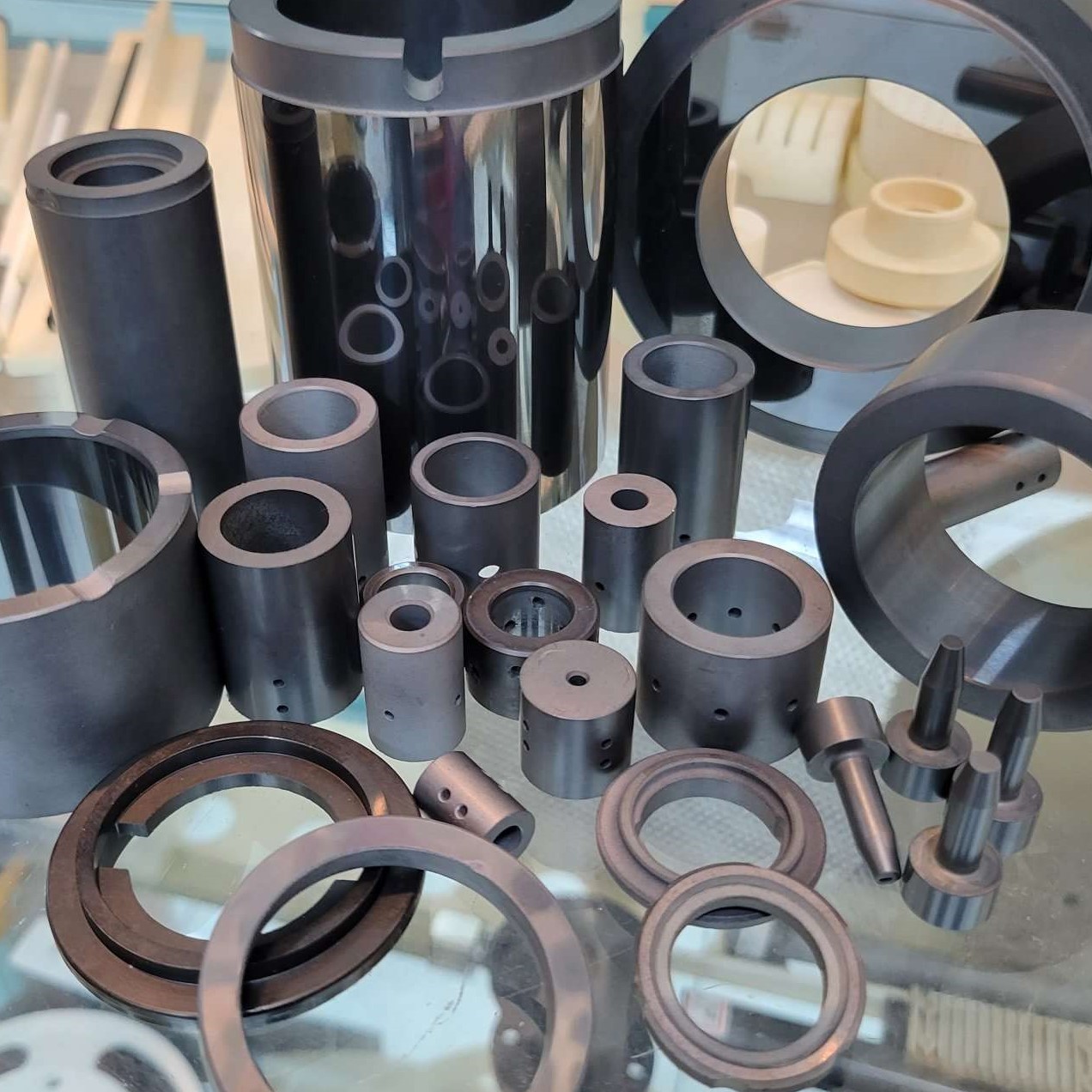
In the field of structural ceramics, zirconia ceramics are widely used due to their high toughness, high flexural strength, high wear resistance, excellent thermal insulation properties, and a thermal expansion coefficient close to that of steel. Key applications include:
Y-TZP grinding balls
Dispersion and grinding media
Nozzles
Ball valve seats
Zirconia molds
Micro-fan shafts
Fiber optic connectors and sleeves
Wire drawing dies and cutting tools
Wear-resistant cutting blades
Clothing buttons
Watch cases and straps
Bracelets and pendants
Ball bearings
Lightweight golf club heads
Other wear-resistant components
Functional Ceramics
Due to its excellent high-temperature resistance, zirconia is used in induction heating tubes, refractory materials, and heating elements. Additionally, zirconia ceramics exhibit sensitive electrical properties, making them suitable for applications such as:
Oxygen sensors
Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC)
High-temperature heating elements
ZrO₂ has a high refractive index (N-21^22). By adding coloring agents (such as V₂O₅, MoO₃, Fe₂O₃, etc.) to ultra-fine zirconia powder, it can be transformed into vibrant, translucent polycrystalline ZrO₂ materials that shimmer like natural gemstones, making them ideal for decorative items.
Furthermore, zirconia is increasingly being applied in:
Thermal barrier coatings
Catalyst supports
Medical and healthcare products
Refractory materials
Textile industry
This versatile material continues to expand its role across various high-tech and industrial fields.
Material Data
Properties | Units | Zirconia(ZrO2) |
| ||||
ZrO2_ Al2O3 | Y2O3-ZrO2 3Y-TZP | Y2O3-ZrO2 8Y-PSZ | Mgo-ZrO2 | ||||
Mechanical | Density | g/cm3 | 4.05 | >6.0 | 5.7 | 5.6 | |
Color | — | White | Ivory / White | Ivory | Yellow/ Ivory | ||
Water Absorption | % | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
Hardness | Gpa | 16 | 12.7 | 6.4 | 12 | ||
Flexural Strength (20°C) | Mpa | 400 | 900 | 280 | 650 | ||
Compressive Strength (20°C) | Mpa | 2500 | 2500 | 1780 | 1800 | ||
Thermal | Thermal Conductivity (20°C) | W/m°k | 20 | 2 | 2.5 | 2 | |
Thermal Shock Resistance (20°C) | ∆T(°C) | 300 | 250 | 500 | 375 | ||
Maximum Use Temperature | °C | 1600 | 1000 | 2400 | 1000 | ||
Electrical | Volume Resistivity (20°C) | Ω-cm | 1012 | 109 | 108 | 1010 | |